Blockchain technology plays a crucial role in preventing fraud and data tampering. With its decentralized and transparent nature, blockchain ensures that every transaction is recorded and verified across multiple computers, making it almost impossible to alter or manipulate data. This makes blockchain a reliable solution that can protect against fraudulent activities and ensure the integrity of data. By providing a secure and tamper-proof framework, blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize various industries and enhance trust in digital transactions.
Blockchain technology has emerged as a revolutionary solution in the fight against fraud and data tampering. Its ability to create a transparent and immutable ledger has captivated industries across the globe. But how exactly does it work? Let’s delve into the intriguing world of blockchain and discover the key role it plays in preventing fraudulent activities and safeguarding data integrity.
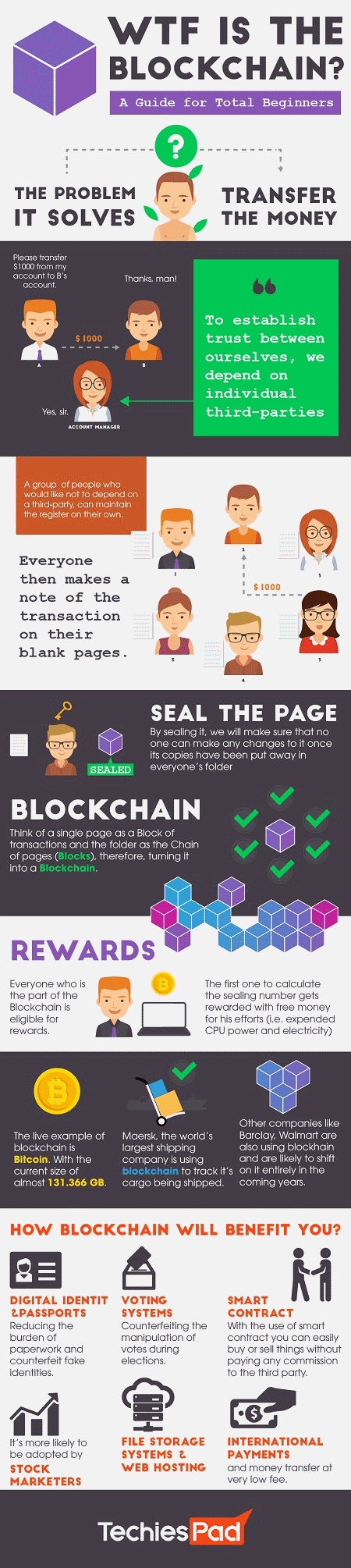
Blockchain, at its core, is a decentralized digital ledger that records transactions in a secure and transparent manner. Each transaction is grouped into a block, which is then added to a chain of previous blocks, forming a permanent and unalterable record. This decentralized nature ensures that no single entity has control over the entire network, making it highly resistant to fraud. In fact, a study by the Association of Certified Fraud Examiners revealed that companies using blockchain technology experienced a 42% reduction in fraud cases. With its tamper-proof design and distributed consensus mechanism, blockchain has become a powerful tool in combating fraud and data manipulation.

Introduction to Blockchain and Its Role in Preventing Fraud and Data Tampering
Blockchain technology has gained significant attention in recent years, revolutionizing various industries with its decentralized and secure nature. One of the key advantages of blockchain is its ability to prevent fraud and data tampering. In this article, we will explore how blockchain technology works and its role in preventing these common challenges.
Blockchain is a distributed ledger technology that enables the secure and transparent recording of transactions across multiple computers or nodes. The information is stored in a chain of blocks, each containing a set of data and a unique cryptographic hash. This cryptographic hash ensures the integrity and immutability of the data, making it highly resistant to fraud and tampering.
By leveraging blockchain technology, businesses and organizations can establish trust, enhance security, and eliminate the need for intermediaries in verifying transactions. Let’s delve deeper into the various ways in which blockchain prevents fraud and data tampering, and its implications for different sectors.
1. Data Immutability and Transparency in Blockchain
One of the fundamental characteristics of blockchain is its immutability. Once data is recorded in a block and added to the chain, it becomes virtually impossible to alter or manipulate without the consensus of the network participants. This immutability ensures that the data remains tamper-proof and trustworthy.
Every transaction recorded on the blockchain is transparent and visible to all network participants. This transparency eliminates the need for trust in centralized authorities or intermediaries, as anyone can verify the authenticity and integrity of the data independently. This level of transparency helps prevent fraud and ensures that all transactions are conducted in a fair and accountable manner.
For example, in the financial sector, blockchain can help prevent fraudulent activities such as double-spending or manipulating financial records. Each transaction on the blockchain is recorded in a transparent and immutable manner, allowing auditors and regulators to easily trace and verify the flow of funds. This transparency promotes trust among users and reduces the risk of fraudulent activities.
Key Takeaways:
- Blockchain technology provides data immutability, making it highly resistant to tampering or fraud.
- Transparent nature of blockchain ensures accountability and trust in transactions.
- In the financial sector, blockchain helps prevent double-spending and promotes transparency in financial transactions.
2. Consensus Mechanisms and Network Security
In a blockchain network, consensus mechanisms play a crucial role in ensuring the security and integrity of the data. Consensus mechanisms are algorithms that enable network participants to agree on the validity of transactions and reach a consensus on the state of the blockchain.
One widely used consensus mechanism is Proof of Work (PoW), which requires participants, known as miners, to solve complex mathematical puzzles to validate transactions and add blocks to the chain. This process is resource-intensive and time-consuming, making it difficult for malicious actors to manipulate the blockchain.
Another consensus mechanism is Proof of Stake (PoS), where participants can mine or validate blocks based on the number of coins they hold. This approach reduces the energy consumption associated with PoW and encourages participants to act in the best interest of the network. Additionally, PoS provides a higher level of security against 51% attacks, where an attacker gains control of the majority of the network’s computing power.
The consensus mechanisms used in blockchain networks ensure the security and integrity of the data by making it computationally expensive to tamper with the blockchain. This enhances the overall security of transactions and prevents fraud or data tampering.
Key Takeaways:
- Consensus mechanisms such as Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS) ensure the security and integrity of the blockchain.
- PoW makes it difficult for malicious actors to manipulate the blockchain due to the resource-intensive nature of mining.
- PoS reduces energy consumption and provides a higher level of security against 51% attacks.
3. Smart Contracts and Automation
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with predefined rules and conditions written directly into the code of the blockchain. These contracts automatically execute when the specified conditions are met, eliminating the need for intermediaries or manual intervention.
Smart contracts enable automated transactions and provide an additional layer of security against fraud and tampering. Once a smart contract is deployed on the blockchain, it cannot be altered or manipulated, ensuring that the agreed-upon terms are enforced without the risk of manipulation.
For example, in supply chain management, smart contracts can automate and streamline the verification and validation processes. By recording each stage of the supply chain on the blockchain, participants can track the movement of goods, verify their authenticity, and ensure compliance with quality standards. This automation reduces the risk of fraudulent activities, such as counterfeit products, and improves overall supply chain transparency.
Key Takeaways:
- Smart contracts automate transactions based on predefined rules and conditions.
- Smart contracts provide an additional layer of security and eliminate the need for intermediaries.
- In supply chain management, smart contracts improve transparency and reduce the risk of fraudulent activities.
4. Blockchain Applications in Various Sectors
The potential applications of blockchain technology in preventing fraud and data tampering extend beyond the financial sector. Let’s explore some of the key industries where blockchain is making an impact:
a. Healthcare:
In the healthcare industry, blockchain can improve data integrity, privacy, and the secure sharing of medical records. It can prevent fraud through secure patient identification, reduce the risk of counterfeit drugs, and ensure accurate clinical trials data.
b. Supply Chain Management:
Blockchain can revolutionize supply chain management by providing end-to-end visibility and transparency. It enables the tracking of products from their origin to the end consumer, ensuring authenticity, preventing counterfeit goods, and reducing the risk of fraud.
c. Identity Management:
Identity management is another area where blockchain can play a crucial role in preventing fraud. By providing a decentralized and tamper-proof identity management system, blockchain technology can prevent identity theft, enable secure digital identities, and protect personal data.
d. Voting Systems:
Blockchain has the potential to revolutionize voting systems by ensuring the integrity of voter registration and eliminating the possibility of tampering with the vote count. It can improve transparency and trust in electoral processes, preventing fraud and ensuring fair elections.
e. Real Estate:
In the real estate industry, blockchain can prevent fraudulent property transactions, enhance the efficiency of title transfers, and enable more secure and transparent property ownership records.
f. Intellectual Property:
Blockchain can protect intellectual property rights by securely registering trademarks, copyrights, and patents. It can create an immutable record of ownership, preventing fraud and ensuring proper recognition and compensation for creators.
g. Insurance:
In the insurance industry, blockchain technology can streamline claims processing, prevent fraudulent claims, and improve overall transparency. By automating the verification and validation of claims, blockchain reduces the risk of fraudulent activities and ensures faster and fairer settlements.
h. Government Services:
Blockchain can enhance the efficiency, transparency, and security of government services, such as land registry, tax administration, identity verification, and public procurement. It can streamline processes, eliminate bureaucracy, and reduce the risk of corruption and fraud.
i. Cybersecurity:
Blockchain technology can strengthen cybersecurity by providing a decentralized and tamper-proof system for storing sensitive information, such as digital certificates, passwords, and authentication credentials. It reduces the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access, ensuring the integrity and confidentiality of data.
j. Energy:
In the energy sector, blockchain can enable the secure and transparent trading of energy, facilitate peer-to-peer energy transactions, and enhance the efficiency of energy management systems. It can prevent fraudulent activities and promote renewable energy integration.
k. Legal:
Blockchain technology has the potential to transform the legal industry by enabling secure and transparent documentation, contract execution, and dispute resolution. It can reduce the risk of fraud, improve the efficiency of legal processes, and enhance trust in legal transactions.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology has emerged as a powerful tool in preventing fraud and data tampering across various sectors. Its inherent characteristics such as data immutability, transparency, consensus mechanisms, and smart contracts provide a secure and trustworthy environment for transactions. The potential applications of blockchain extend beyond finance, with industries like healthcare, supply chain management, identity management, and voting systems benefiting from its capabilities.
As blockchain technology continues to evolve and mature, we can expect to see further advancements in preventing fraud and data tampering, ultimately leading to increased trust, improved security, and enhanced efficiency in a wide range of industries.
To learn more about building decentralized applications or explore real-world applications of blockchain technology, visit this link.

In conclusion, blockchain technology plays a vital role in preventing fraud and data tampering. With its decentralized and transparent nature, blockchain offers a secure and immutable ledger for recording transactions and information.
By eliminating the need for intermediaries and providing a trusted and tamper-resistant system, blockchain instills trust and confidence in the digital world. It ensures the integrity and authenticity of data, making it an effective tool in preventing fraud and safeguarding sensitive information.


