Data governance plays a crucial role in ensuring the quality and compliance of data. With the ever-increasing volume and complexity of data, organizations need effective strategies to manage and protect their data assets. Did you know that poor data quality costs businesses an average of $15 million per year? This staggering statistic highlights the importance of implementing robust data governance practices to mitigate risks and drive better business outcomes.
The evolution of data governance has witnessed significant advancements over the years. Initially, it focused on establishing processes and policies to ensure data accuracy and consistency. However, in today’s data-driven world, data governance has expanded to encompass regulatory compliance, security, and privacy concerns. Organizations are now adopting technologies like artificial intelligence and machine learning to automate data governance processes, enhancing data quality and compliance. This holistic approach not only helps organizations meet regulatory requirements but also enables them to gain valuable insights from their data, leading to improved decision-making and innovation.
.png)
The Evolution of Data Governance: Ensuring Data Quality and Compliance
Data governance is a critical aspect of managing and utilizing data effectively within organizations. It involves the strategic planning and implementation of policies, procedures, and guidelines to ensure the accuracy, integrity, and security of data. Data governance has evolved significantly over the years, driven by technological advancements, regulatory requirements, and the increasing importance of data-driven decision-making. In this article, we will explore the evolution of data governance and its role in ensuring data quality and compliance.
As organizations have become more reliant on data for decision-making, the need for effective data governance has become paramount. In the past, data governance primarily focused on data quality and compliance with regulations. However, with the proliferation of data sources, the rise of big data, and the emergence of new technologies such as cloud computing and artificial intelligence, data governance has evolved to encompass a broader set of responsibilities.
Today, data governance not only involves ensuring the accuracy, completeness, and consistency of data but also encompasses data privacy, security, and ethics. It covers the entire data lifecycle, from data collection and storage to data analysis and reporting. Data governance frameworks and processes are designed to establish control over data assets and ensure that data is managed in a way that aligns with organizational goals and regulatory requirements.
Want to learn more about navigating the world of cloud-based software solutions? Check out this informative article for valuable insights.
The Importance of Data Quality in Data Governance
Data quality is a fundamental aspect of data governance. High-quality data is accurate, complete, consistent, and reliable, making it essential for informed decision-making and business operations. Poor data quality can lead to costly mistakes, misinformed decisions, and reputational damage for organizations.
In the early stages of data governance, data quality was often an afterthought, with organizations focusing more on data collection and storage. However, as the volume and complexity of data increased, so did the importance of data quality. Organizations realized that without accurate and reliable data, their decision-making processes and business operations would be severely compromised.
To ensure data quality, organizations implement data governance processes and practices such as data profiling, data cleansing, and data validation. Data profiling involves assessing the quality of data by examining its structure, completeness, and consistency. Data cleansing refers to the process of identifying and correcting data errors, inconsistencies, and duplicates. Data validation involves verifying that data meets predefined standards and rules.
Data quality is not a one-time effort but an ongoing process that requires continuous monitoring and improvement. With the evolution of data governance, organizations have realized the need to invest in data quality tools, technologies, and resources to ensure that high-quality data is available for decision-making and business operations.
Ensuring Data Compliance in Data Governance
Data compliance is another critical aspect of data governance, particularly in industries with stringent regulatory requirements such as finance, healthcare, and telecommunications. Compliance involves adhering to industry-specific regulations and standards to protect the privacy, security, and integrity of data.
In the early stages of data governance, compliance was mainly focused on meeting regulatory requirements and avoiding penalties or legal consequences. However, as data breaches and privacy scandals became more prevalent, organizations began to realize the importance of proactively managing data compliance.
With the advent of new regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), data compliance has become even more critical. These regulations place strict requirements on organizations regarding the collection, storage, processing, and sharing of personal data. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in significant fines and reputational damage.
To ensure data compliance, organizations need to develop robust data governance frameworks and processes that align with regulatory requirements. This includes implementing data protection measures, obtaining consent for data collection and processing, establishing data retention policies, and conducting regular audits and assessments to ensure ongoing compliance.
Data compliance is an ongoing effort that requires continuous monitoring, training, and adaptation to changing regulations. With the evolution of data governance, organizations are leveraging technologies such as data encryption, access controls, and data classification to enhance data security and compliance.
The Future of Data Governance: Emerging Trends and Challenges
As data continues to grow in volume, variety, and velocity, the future of data governance will be shaped by emerging trends and challenges. Here are some key trends and challenges to consider:
1. Big Data and Data Analytics
The rise of big data and data analytics presents both opportunities and challenges for data governance. On one hand, organizations can harness the power of big data and advanced analytics to gain valuable insights and drive innovation. On the other hand, managing and governing large volumes of data can be complex and resource-intensive.
Data governance frameworks and processes will need to evolve to accommodate the unique characteristics of big data, such as its velocity, variety, and veracity. Organizations will need to invest in technologies and platforms that enable efficient data governance and provide real-time insights into data quality, usage, and lineage.
2. Privacy and Ethical Considerations
With the increasing focus on data privacy and ethics, data governance will need to address these considerations. Organizations will need to incorporate privacy by design principles into their data governance frameworks, ensuring that data is collected, processed, and shared in a way that respects individual privacy rights.
Ethical considerations, such as the responsible use of data and the avoidance of bias in algorithms and models, will also become central to data governance. Organizations will need to establish guidelines and practices that promote ethical data use and ensure transparency and accountability.
3. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) technologies introduces new challenges and opportunities for data governance. AI and ML algorithms rely on vast amounts of data to train and make predictions, which raises questions about data quality, bias, and privacy.
Data governance will need to address these issues by ensuring that data used for AI and ML is accurate, representative, and unbiased. Organizations will also need to establish mechanisms to monitor and control AI and ML models to ensure compliance with ethical, legal, and regulatory requirements.
4. Data Democratization
Data democratization, or the ability to provide access to data and insights to a broader audience, is an emerging trend in data governance. As more employees and stakeholders require access to data, organizations will need to implement data governance practices that balance data accessibility with data security and compliance.
Data governance frameworks will need to include mechanisms for data access control, data sharing, and data literacy to ensure that users have the necessary skills and understanding to make informed decisions based on the data.
Ensuring Data Quality and Compliance in the Evolving Landscape
In conclusion, the evolution of data governance has been driven by the increasing importance of data in decision-making, advancements in technology, and the need to comply with regulatory requirements. Data governance has expanded beyond data quality and compliance to encompass privacy, security, and ethics.
As organizations navigate the evolving landscape of data governance, they must prioritize data quality and compliance to ensure the accuracy, integrity, and security of their data. By implementing robust data governance frameworks, leveraging technologies and tools, and staying abreast of emerging trends and challenges, organizations can effectively manage their data assets and drive informed decision-making.
For more information on navigating the world of cloud-based software solutions, check out this informative article.
The Evolution of Data Governance: Ensuring Data Quality and Compliance
- Data governance is the process of managing and ensuring the quality, integrity, and security of data within an organization.
- Data governance has evolved over time to keep up with advancements in technology and the increasing volume of data generated.
- Ensuring data quality is crucial for organizations as it helps in making accurate business decisions and reducing risk.
- Data compliance refers to adhering to regulations and policies related to data privacy, security, and usage.
- Implementing a robust data governance framework helps organizations meet compliance requirements and maintain the trust of customers and stakeholders.
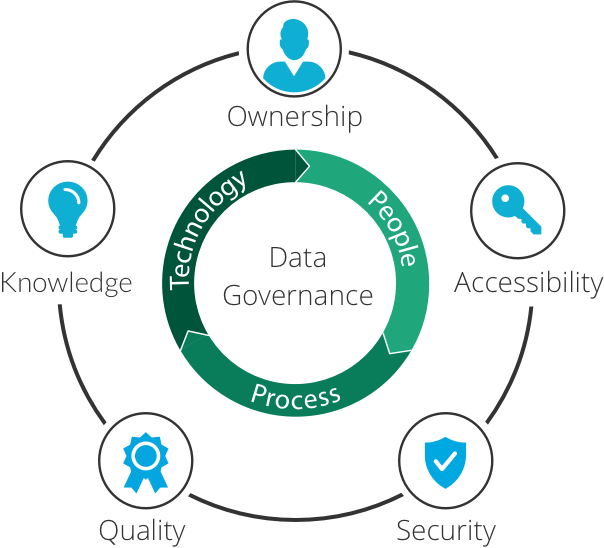
Data governance is the process of managing and protecting data to ensure its quality and compliance.
It has evolved over time to become an essential practice for businesses in the digital age.
Data governance involves establishing policies, processes, and responsibilities to ensure data is accurate, secure, and used appropriately.
This helps organizations make informed decisions, maintain customer trust, and meet regulatory requirements.
Data governance also addresses data privacy concerns, such as the protection of personally identifiable information (PII).
By implementing data governance practices, companies can minimize data breaches, reduce financial and reputational risks, and enhance their overall data management capabilities.
In conclusion, data governance is crucial for ensuring data quality and compliance in the digital age.


