Edge computing has revolutionized data processing, bringing new possibilities and capabilities to businesses. By processing data closer to the source, edge computing reduces latency and improves real-time analytics, making it ideal for industries such as IoT, retail, and healthcare. With its distributed architecture, edge computing enhances security and reduces bandwidth reliance. Moreover, it enables faster decision-making, scalability, and cost-efficiency. Embracing edge computing is essential for companies looking to harness the power of data processing in the modern age.
As technology continues to advance at a rapid pace, the demand for faster and more efficient data processing has become paramount. One solution that has emerged to meet this need is edge computing. Edge computing refers to the decentralized processing of data at the edge of the network, closer to where it is being generated. This allows for quicker data analysis and response time, reducing latency and improving overall performance.
With the exponential growth of connected devices and the Internet of Things (IoT), edge computing has become increasingly essential in redefining data processing. By bringing computation and data storage closer to the source, edge computing enables real-time insights and decision-making without the need to send data back and forth to a central server. This not only reduces bandwidth and latency issues but also enhances security and privacy by minimizing the exposure of sensitive data. In fact, according to a report by Gartner, by 2025, 75% of enterprise-generated data will be processed outside traditional data centers, largely due to the adoption of edge computing solutions.
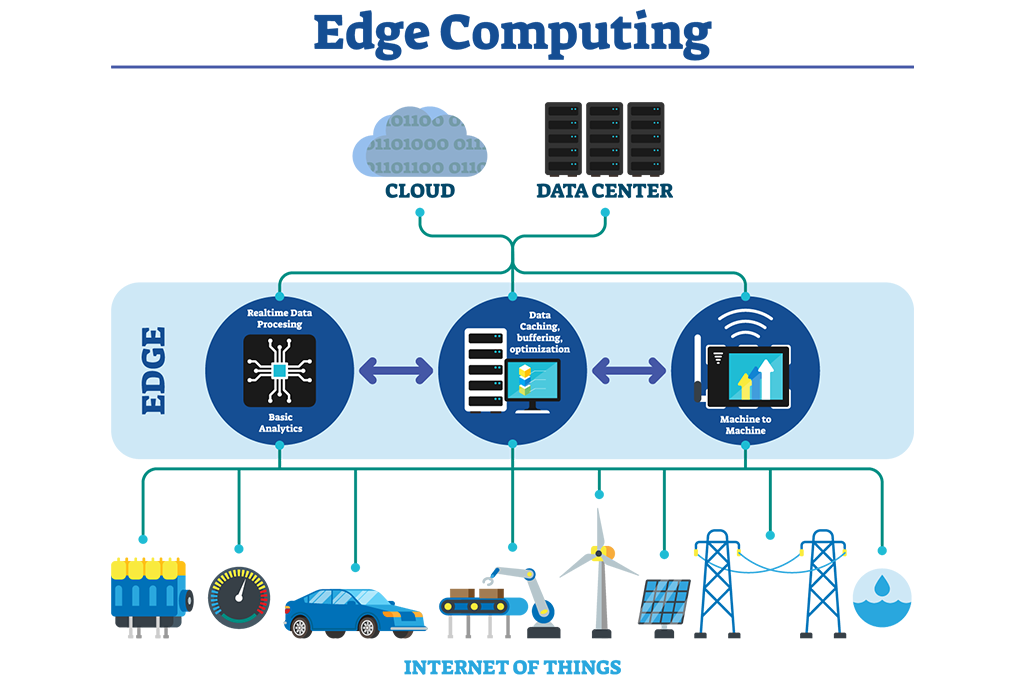
The Power of Edge Computing: Improving Data Processing Efficiency
Edge computing is revolutionizing the world of data processing, offering a new approach to handling vast amounts of information in real-time. Traditional cloud-based data processing involves sending data to a centralized server or data center for analysis and processing. However, this approach can introduce significant latency and bandwidth limitations, especially when dealing with large amounts of data or time-sensitive applications.
Edge computing addresses these challenges by bringing data processing closer to the source, reducing latency and improving efficiency. The key concept behind edge computing is to perform data processing and analysis at the edge of the network, closer to where the data is generated. By leveraging edge devices such as gateways, routers, or even specialized edge servers, organizations can process data locally, enabling faster response times and reducing the burden on centralized data centers.
One significant advantage of edge computing is its ability to support real-time applications that require immediate processing and response. For example, in the context of autonomous vehicles, edge computing enables real-time analysis of sensor data, allowing the vehicle to make split-second decisions without relying on a distant server. This capability is also crucial for industries such as healthcare, where data processing delays can have life-or-death consequences.
Reducing Latency for Time-Sensitive Applications
One of the primary benefits of edge computing is its ability to reduce latency for time-sensitive applications. In scenarios where real-time processing is critical, such as autonomous vehicles, industrial automation, or augmented reality, minimizing latency is crucial for optimal performance. With traditional cloud-based approaches, data must travel to and from a central data center, causing delays in decision-making and responsiveness.
Edge computing solves this problem by moving data processing closer to the edge of the network, near where the data is generated. This proximity allows for faster data processing and analysis, enabling real-time decision-making. For example, in the case of autonomous vehicles, edge computing helps process sensor data on the vehicle itself or nearby edge devices, allowing for quick responses to changing road conditions and ensuring passenger safety.
Moreover, reducing latency is also crucial for various Internet of Things (IoT) applications, where devices generate massive amounts of data in real-time. Edge computing enables efficient data filtering and processing at the edge, significantly reducing network congestion and minimizing the need to transfer large volumes of data to the cloud. This approach not only improves the overall performance of IoT systems but also reduces bandwidth costs and enhances scalability.
Enhancing Data Privacy and Security
Another significant advantage of edge computing is its ability to enhance data privacy and security. By processing data locally at the edge, organizations can reduce the risk of sensitive information being exposed or intercepted during transit to a centralized cloud server. This localized processing also allows for localized data storage, further minimizing the potential attack surface.
In addition, edge computing can implement data encryption and security measures directly at the edge devices themselves, ensuring that information remains secure throughout the entire data processing pipeline. This decentralized approach to data processing and storage reduces the reliance on a single point of failure, making it more challenging for malicious actors to compromise the system or gain unauthorized access to sensitive data.
Furthermore, edge computing can provide significant advantages in industries where data privacy regulations or compliance requirements restrict the movement of sensitive data to the cloud. For example, in healthcare, patient data is subject to strict privacy regulations, and processing it locally at the edge can help organizations meet compliance requirements while still leveraging the benefits of data analysis and real-time insights.
Enabling Offline Data Processing
A key feature of edge computing is its ability to support offline data processing, allowing organizations to continue functioning even in situations where network connectivity is limited or unreliable. In traditional cloud-based approaches, the reliance on an internet connection means that data processing and analysis may be disrupted if connectivity is lost.
With edge computing, on the other hand, organizations can perform data processing and analysis locally, even in the absence of an internet connection. This capability is particularly useful in remote or mobile environments, such as offshore oil rigs or connected vehicles that operate in areas with limited network coverage. By processing data locally, organizations can maintain continuity and make critical decisions without relying on a constant internet connection.
Additionally, offline data processing also helps reduce bandwidth usage and associated costs. By processing data locally, organizations can filter and aggregate information before sending it to the cloud, minimizing the amount of data that needs to be transmitted. This approach is especially valuable in scenarios where internet connectivity is expensive or unreliable, enabling optimized data transfer and reducing reliance on costly network infrastructure.
Improving Scalability and Cost Efficiency
Edge computing offers significant benefits in terms of scalability and cost efficiency. By distributing data processing closer to the source, edge computing minimizes the need for expensive and resource-intensive centralized data centers. Instead of relying solely on the cloud for processing power and storage, organizations can harness the computational capabilities of edge devices distributed throughout their network.
This distributed approach to computing allows organizations to scale their data processing capabilities more effectively. As the volume of data generated increases, additional edge devices can be deployed to handle the workload, ensuring optimal performance and minimal latency. This scalability is crucial for industries that experience rapid data growth, such as manufacturing, logistics, or smart cities.
Moreover, edge computing can also help reduce costs by minimizing the amount of data that needs to be transmitted and stored in the cloud. By processing and filtering the data at the edge, organizations can reduce network bandwidth requirements and optimize storage usage. This approach not only reduces operational costs associated with data transfer but also helps avoid unnecessary expenses related to storing and processing irrelevant or low-value data.
Optimizing Network Bandwidth with Edge Computing
Edge computing plays a crucial role in optimizing network bandwidth usage, especially in scenarios where data is generated at the edge of the network. In traditional cloud-based architectures, sending large volumes of data to a central server for processing can strain the network and lead to bandwidth bottlenecks. This is particularly challenging in environments with limited network infrastructure or high data generation rates.
By leveraging edge computing, organizations can reduce the burden on network bandwidth by processing data locally, closer to the source. Localized data processing and analysis at the edge minimize the need to transfer large datasets over long distances, freeing up network capacity for other critical tasks. This optimization of network bandwidth enhances overall system performance, reduces latency, and ensures faster data processing and analysis.
To illustrate this point, consider the example of a smart city infrastructure with numerous sensors and devices generating vast amounts of data. By implementing edge computing, the localized processing at the edge devices can reduce the amount of data that needs to be sent to a central cloud server, thereby alleviating the strain on the network infrastructure and ensuring timely response to events or alerts.
Enabling Real-Time Analytics and Insights
Edge computing enables organizations to leverage real-time analytics and gain valuable insights from their data at the edge of the network. By processing data locally, immediate analysis and decision-making can take place, enabling organizations to respond quickly to changing conditions, events, or anomalies.
Real-time analytics at the edge can provide significant advantages in a variety of applications. For instance, in the manufacturing industry, edge computing allows for real-time monitoring and analysis of equipment performance, predictive maintenance, and quality control. By detecting and addressing issues in real-time, organizations can minimize downtime, optimize production efficiency, and reduce maintenance costs.
Furthermore, edge computing also enables closer integration with artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) capabilities. By deploying AI and ML models directly at the edge, organizations can perform real-time inferencing and make data-driven decisions without relying on a central server. This integration of edge computing with AI/ML not only allows for faster analysis and decision-making but also reduces the amount of data that needs to be transmitted back to the cloud for processing, saving bandwidth and reducing latency.
The Future of Edge Computing: Expanding Possibilities
As technology advances and the internet of things continues to grow, the importance of edge computing will only continue to increase. The potential applications of edge computing span a wide range of industries, from autonomous vehicles and smart cities to healthcare and industrial automation.
With the deployment of 5G networks, edge computing is set to become even more powerful, enabling low-latency, high-bandwidth connections for a multitude of edge devices. This combination of edge computing and 5G will pave the way for innovative solutions and services that were previously impractical or impossible.
As organizations embrace the power of edge computing, they will be able to unlock the full potential of their data, improve operational efficiency, enhance security, and deliver real-time insights and experiences to their customers. The era of edge computing is upon us, redefining data processing and shaping the future of technology.
| Header 1 | Header 2 |
| Row 1, Column 1 | Row 1, Column 2 |
| Row 2, Column 1 | Row 2, Column 2 |
The Power of Edge Computing: Redefining Data Processing
- Edge computing brings data processing closer to the source, reducing latency and improving efficiency.
- With edge computing, data can be processed in real-time, enabling faster decision-making.
- Edge computing helps alleviate the strain on cloud resources by processing data locally.
- Edge computing is enabling the growth of IoT devices by providing faster and more reliable data processing.
- Edge computing offers greater data privacy and security by keeping sensitive data at the edge instead of sending it to the cloud.
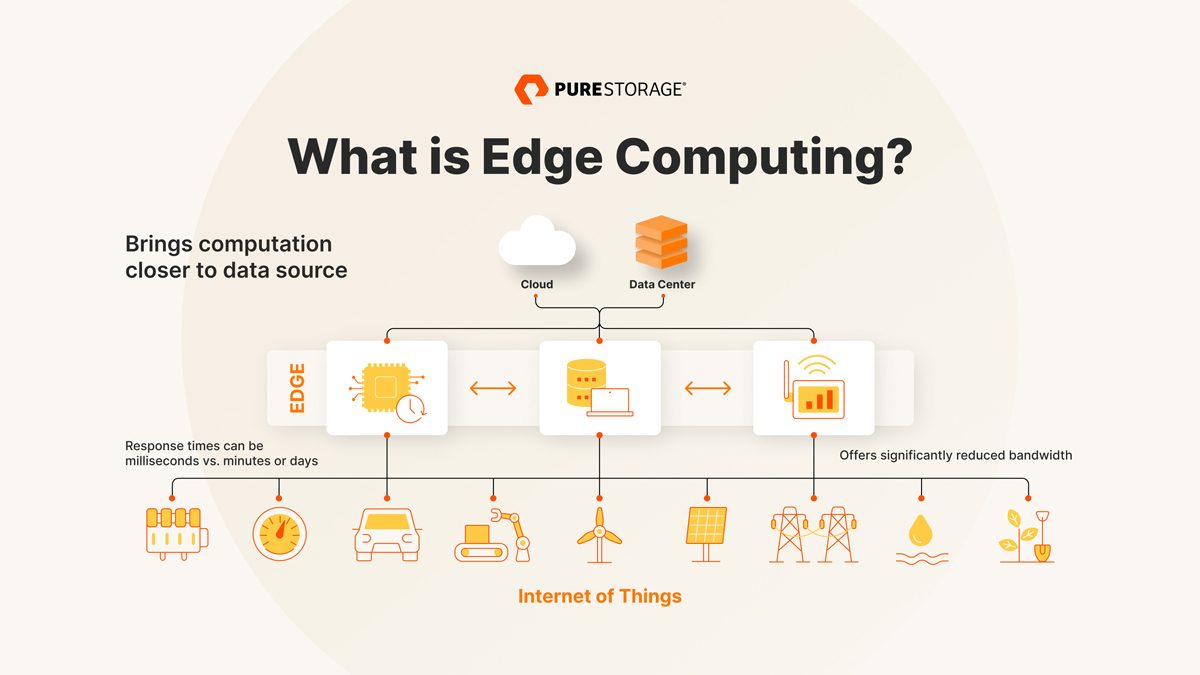
Edge computing is revolutionizing data processing, bringing it closer to where it’s needed.
By moving data processing to the edge of the network, faster and more efficient analysis can be achieved.
With edge computing, data is processed locally on devices or in nearby data centers, reducing latency and improving response times.
This technology is especially beneficial for applications that require real-time insights and quick decision-making.
Furthermore, edge computing enhances data security and privacy by keeping sensitive information closer to the source.
Overall, edge computing is redefining data processing by bringing it closer to the users and devices, enabling faster analysis, improved response times, and enhanced data security.
By harnessing the power of edge computing, businesses and individuals can unlock new possibilities and drive innovation in various industries.


